
Tackling File Transfer with Customers in 2022
Find out how you can manage file transfer with customers to share the information you need. Read More
Published on 23 Sep 2020 - Updated on 07 Dec 2021
When using file transfer protocol, you may want to be aware of the different elements involved. One element is the FTP port. Successful file transfers can only happen when the correct ports are open.

In terms of FTP, ports are communication endpoints. Ports allow the connection and transfer of data to happen between your computer and a server.
To connect to a specific server, you need to know that server’s IP address. While that IP address identifies a particular server, ports are numbers that are used at a lower level to specify what application or service on the server you are trying to communicate with.
IP addresses are unique on the internet to the one server they are assigned to, but ports are a fixed range of numbers from 0 to 65535 that each server uses.

When a service that can accept some remote connection (like an FTP server) starts up, it starts “listening” on a specific port. For common services, there is an expected, set port that the application should be using. The first 1024 ports are reserved for known special services. These services have been assigned a standard port by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).
When a file transfer client makes a connection to a port that a file transfer service is listening on, they can then exchange information. Initially, this is in the form of commands. Commands establish the connection details and operations your want performed. The next step involves transferring the file data requested over the same or a similarly established connection.
The FTP port that you generally need to know about to make a standard, unencrypted, FTP connection is port 21. For this standard case, this is all someone using an FTP client needs to know.
Yes. More ports are used, with differences based on the type of FTP. Other ports are also used in the case of SFTP, which is a totally different protocol.
FTP has been officially assigned ports 20 and 21. If specifically using an “active” connection setting, this means that while a client computer makes the connection request and sends the commands first on port 21, known as the “control port,” a connection to the server on port 20, the “data port,” is also automatically opened to transfer the file data.
If using a “passive” FTP connection setting, the client computer also connects to the server on FTP port 21. However, the server responds with a random port number, in a free range of ports, to use for the data port for file transfers.
For example, your FTP client will open a control channel on port 21 and a data channel on a random high port in the 60000 – 65535 port range.
Implicit FTPS uses different ports by default, starting with the assigned FTPS TCP port 990 to make the control connection. This initiates an SSL/TLS handshake, followed by a connection to port 989 to transfer the encrypted file data.
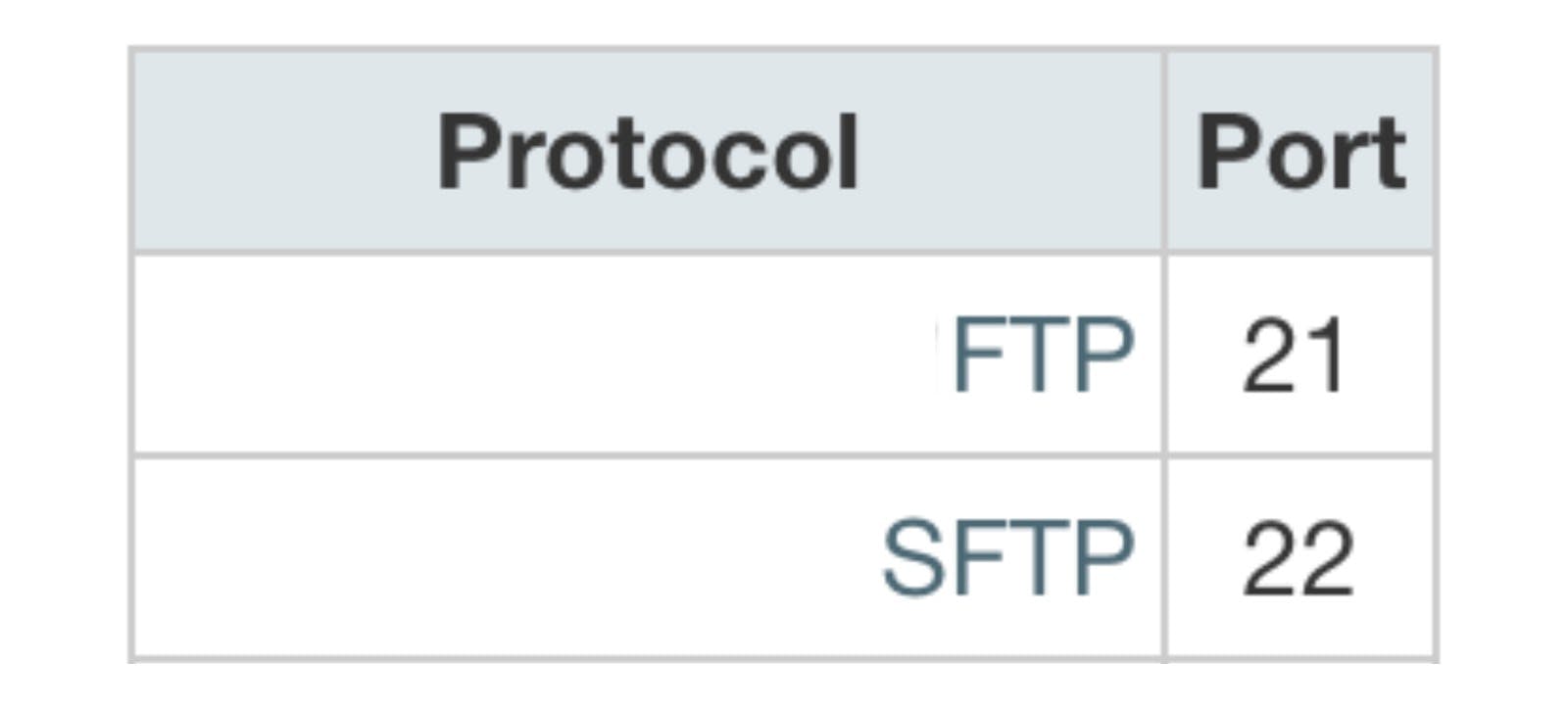
SFTP uses a different port. The SFTP port is 22, the same as an SSH connection. In addition, it uses that same port for both control messages and data transfers.
The reason for this is that SFTP is not directly related to FTP. It is a secure, advanced file transfer protocol over SSH, modeled after the way FTP operates.
By using the SFTP port, both connection credentials and transferred data are always encrypted, ensuring security. Additionally, SSH keys can be used to authenticate a connection, and secure FTP commands providing another layer of protection.
No matter what protocol you are using, the FTP port or other ports opened ensure that you are making the desired connection and that your data transfers efficiently between endpoints.
Looking for FTP or SFTP hosting?
Find out more about ExaVault and start your free trial today!

Find out how you can manage file transfer with customers to share the information you need. Read More

File Transfer Protocol has been around for a long time. But there's also FTPS, FTP-SSL, and SFTP. Read More